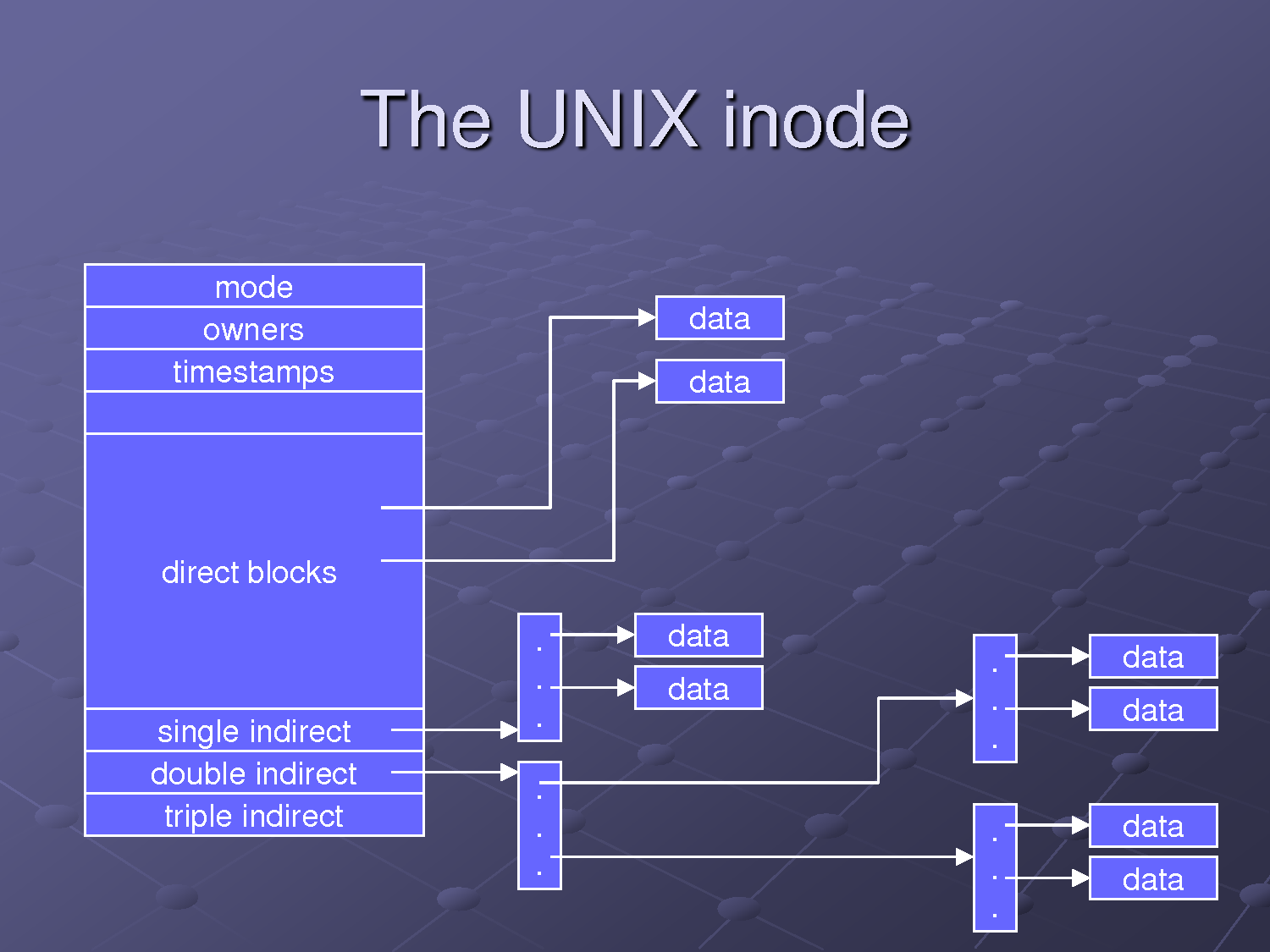
The inode (index node) is a fundamental concept in the Linux and UNIX filesystem. Each object in the filesystem is represented by an inode. But what are the objects? Let us try to understand it in simple words. Each and every file under Linux (and UNIX) has following attributes:
=> File type (executable, block special etc)
=> Permissions (read, write etc)
=> Owner
=> Group
=> File Size
=> File access, change and modification time (remember UNIX or Linux never stores file creation time, this is favorite question asked in UNIX/Linux sys admin job interview)
=> File deletion time
=> Number of links (soft/hard)
=> Extended attribute such as append only or no one can delete file including root user (immutability)
=> Access Control List (ACLs)
All the above information stored in an inode. In short the inode identifies the file and its attributes (as above) . Each inode is identified by a unique inode number within the file system. Inode is also know as index number.
You can use ls -i command to see inode number of file
# ls -li
Output
1324614 -rw——- 1 root root 1529 Oct 6 2009 anaconda-ks.cfg
You can also use stat command to find out inode number and its attribute:
$ stat /etc/passwd
![]()
![]()